Docker Commands
Docker Engine includes the Docker CLI, which provides command-line tools for interacting with the Docker daemon. This document introduces commonly used Docker commands.
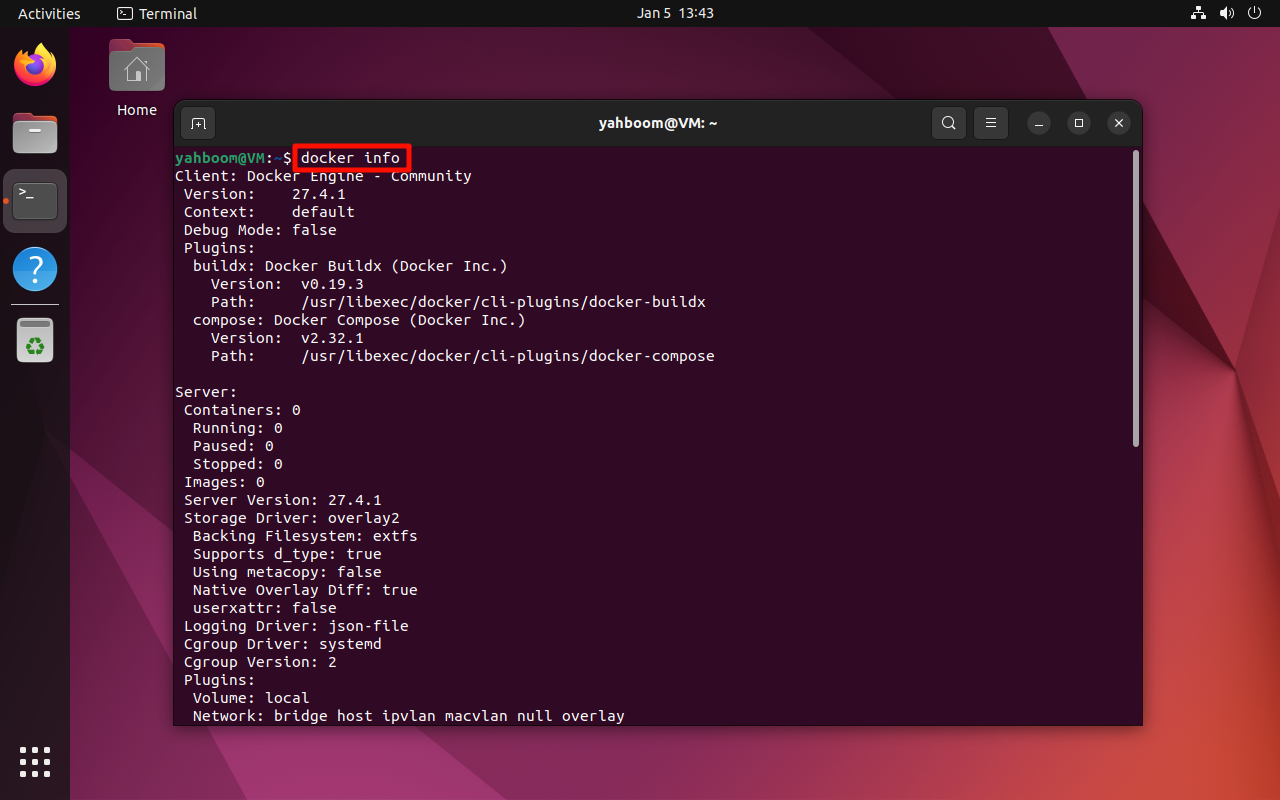
1. View Detailed Information
docker info
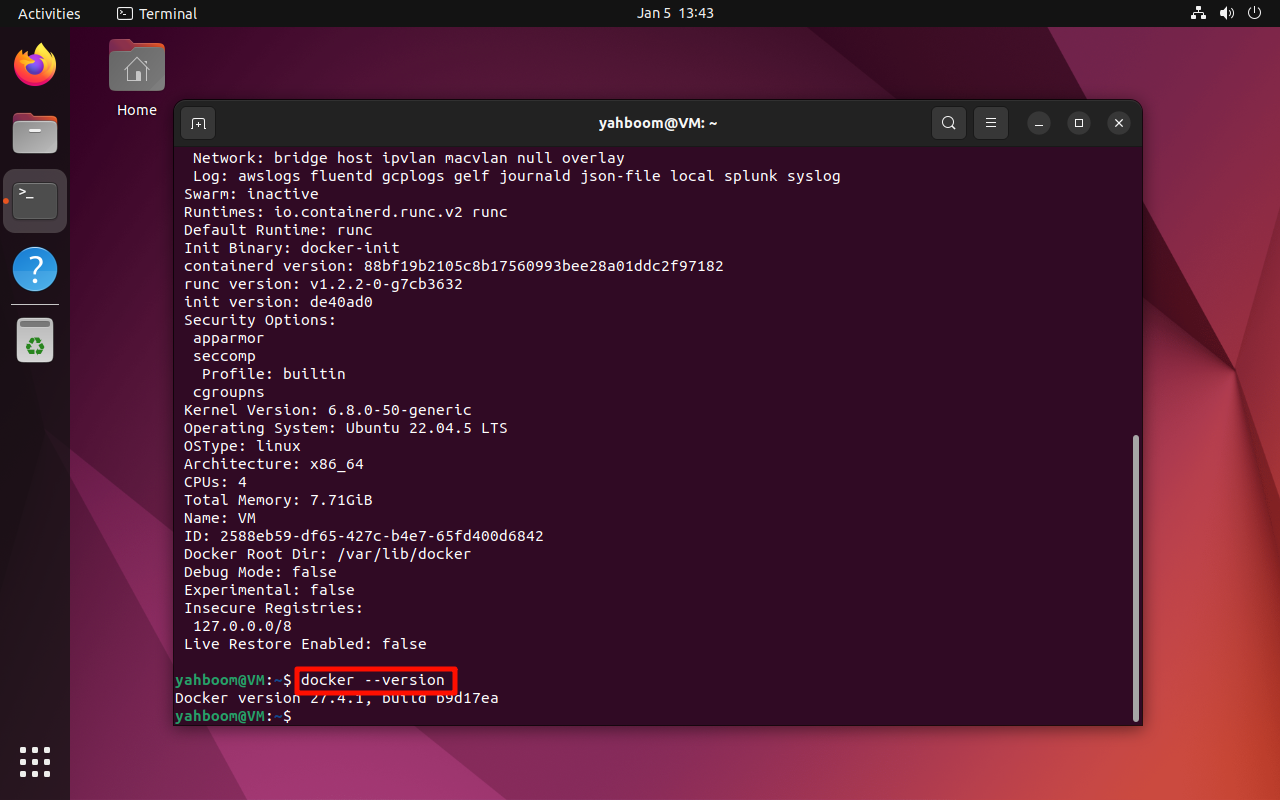
2. View the Version Number
docker --version
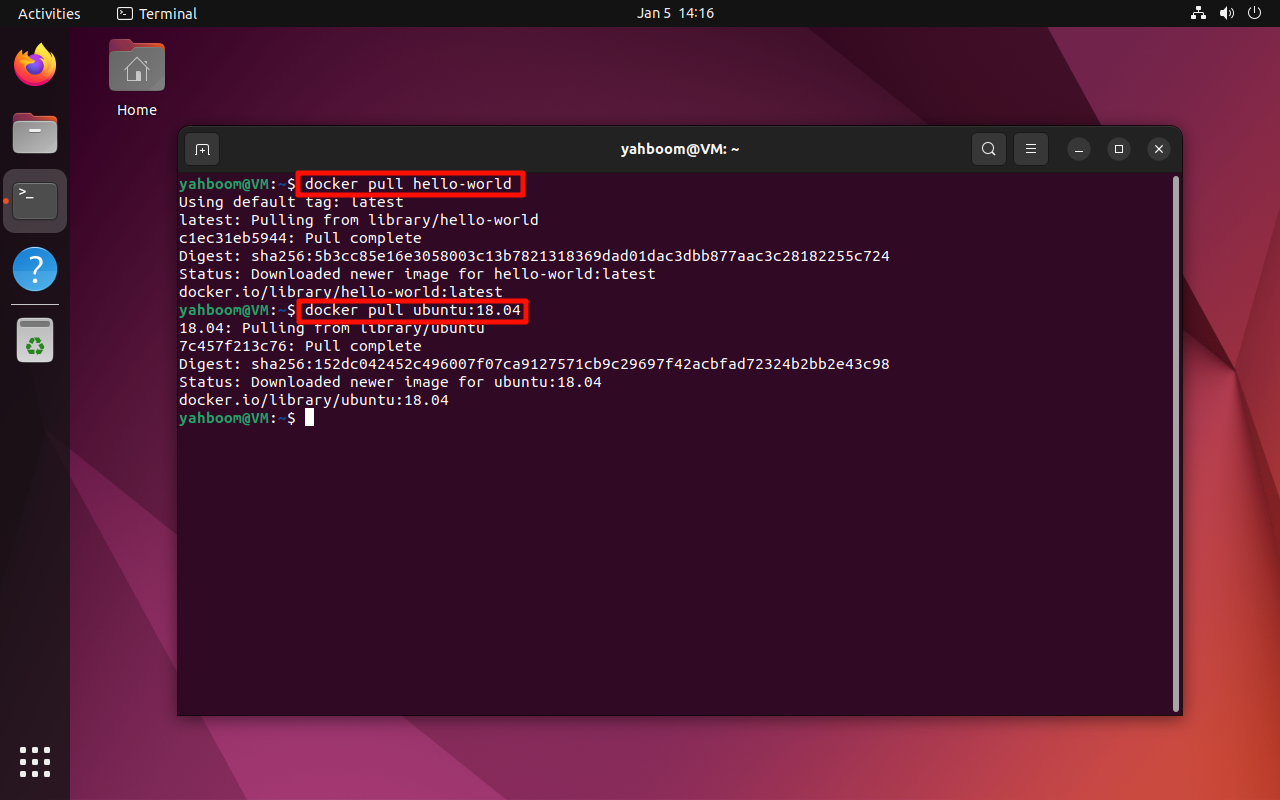
3. Pull an Image
Pull the latest version of an image:
docker pull <image_name>
Example:
docker pull hello-world
Pull a specific tag:
docker pull <image_name>:<tag>
Example:
docker pull ubuntu:18.04
4. Run an Image
If the image does not exist locally, Docker will pull it automatically.
docker run <image_name>
Example:
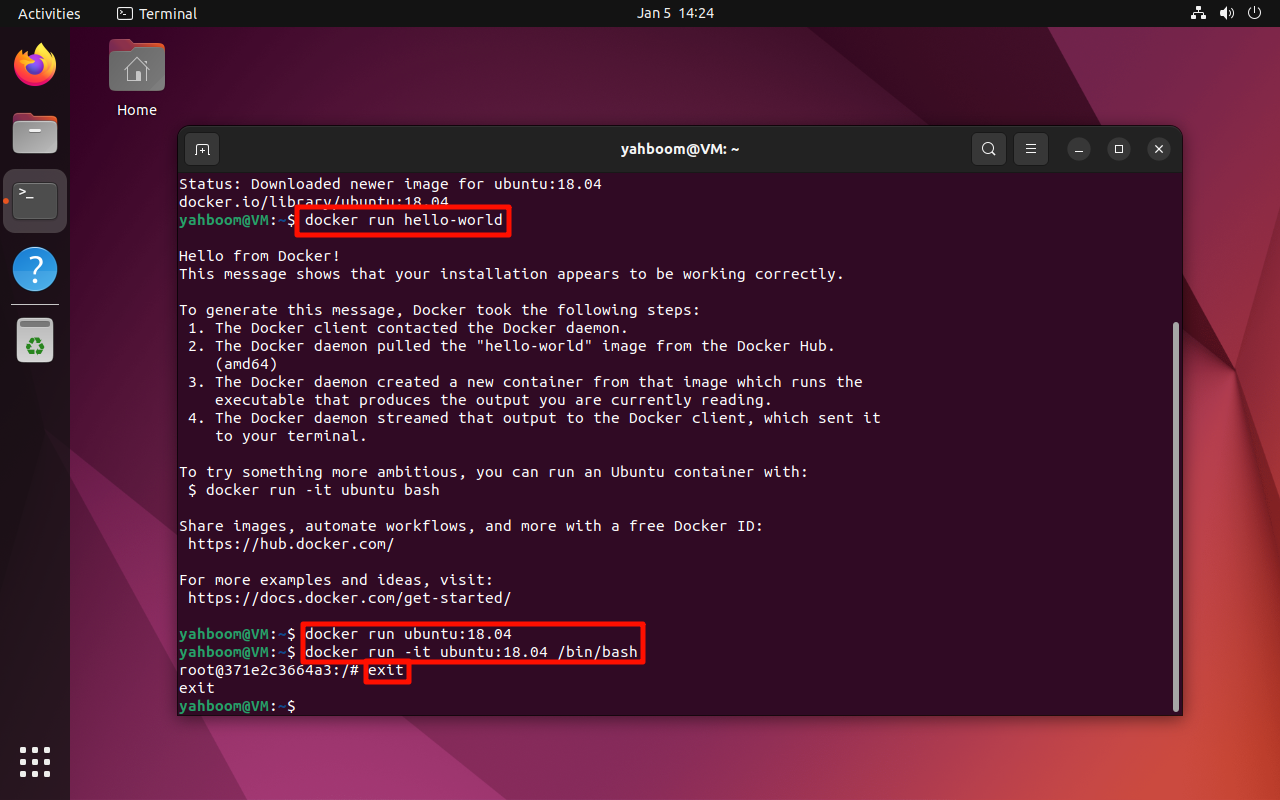
docker run hello-world
Run and exit immediately:
docker run ubuntu:18.04
Run in interactive mode:
docker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
Exit the container with:
exit
4.1 View Running Containers
docker ps
4.2 View All Containers (Running + Stopped)
docker ps -a
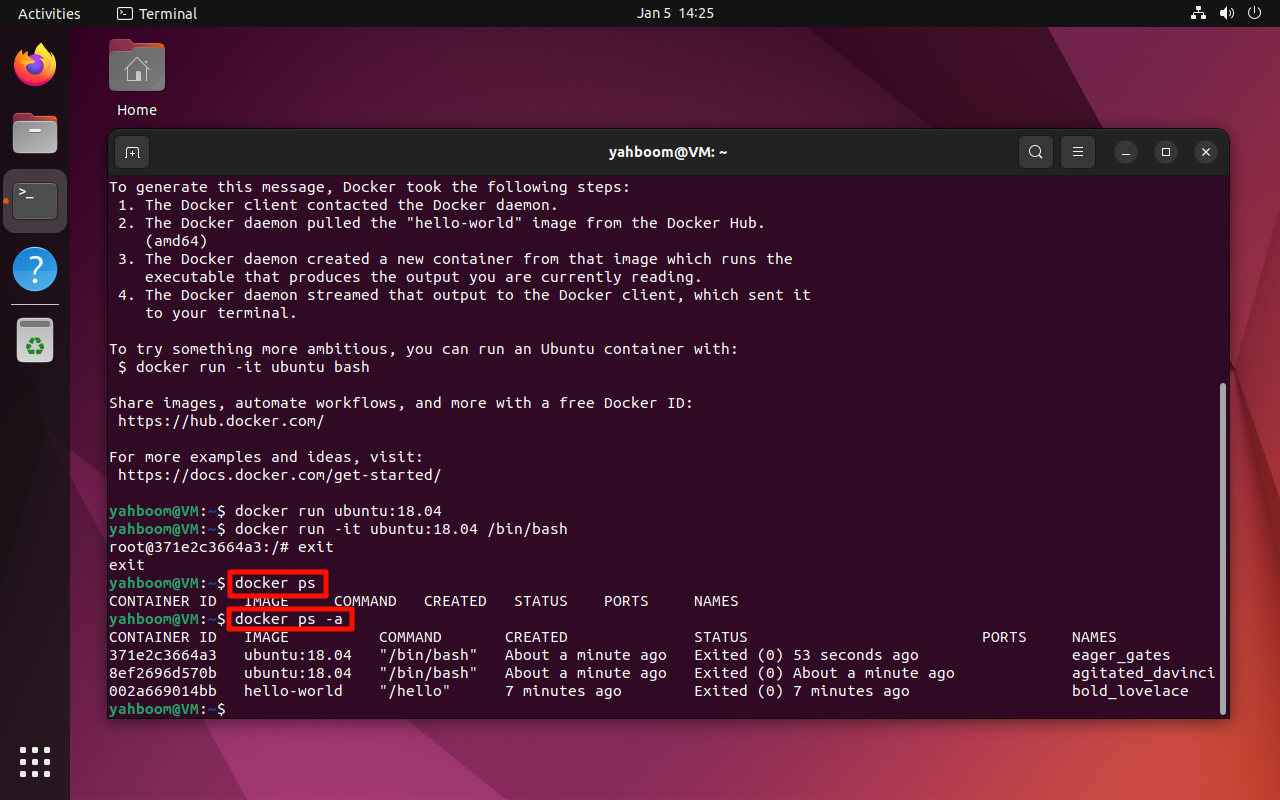
5. Clean Up Containers
Remove all stopped containers:
docker container prune
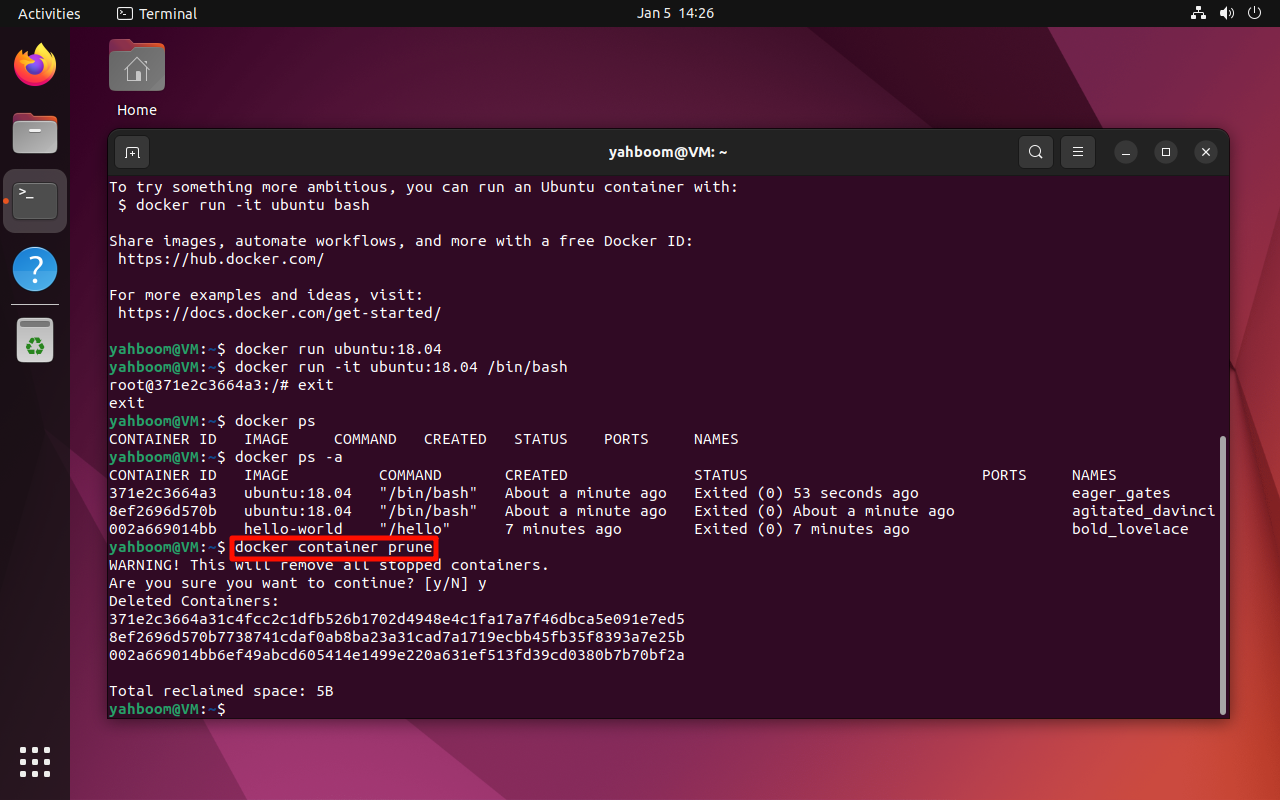
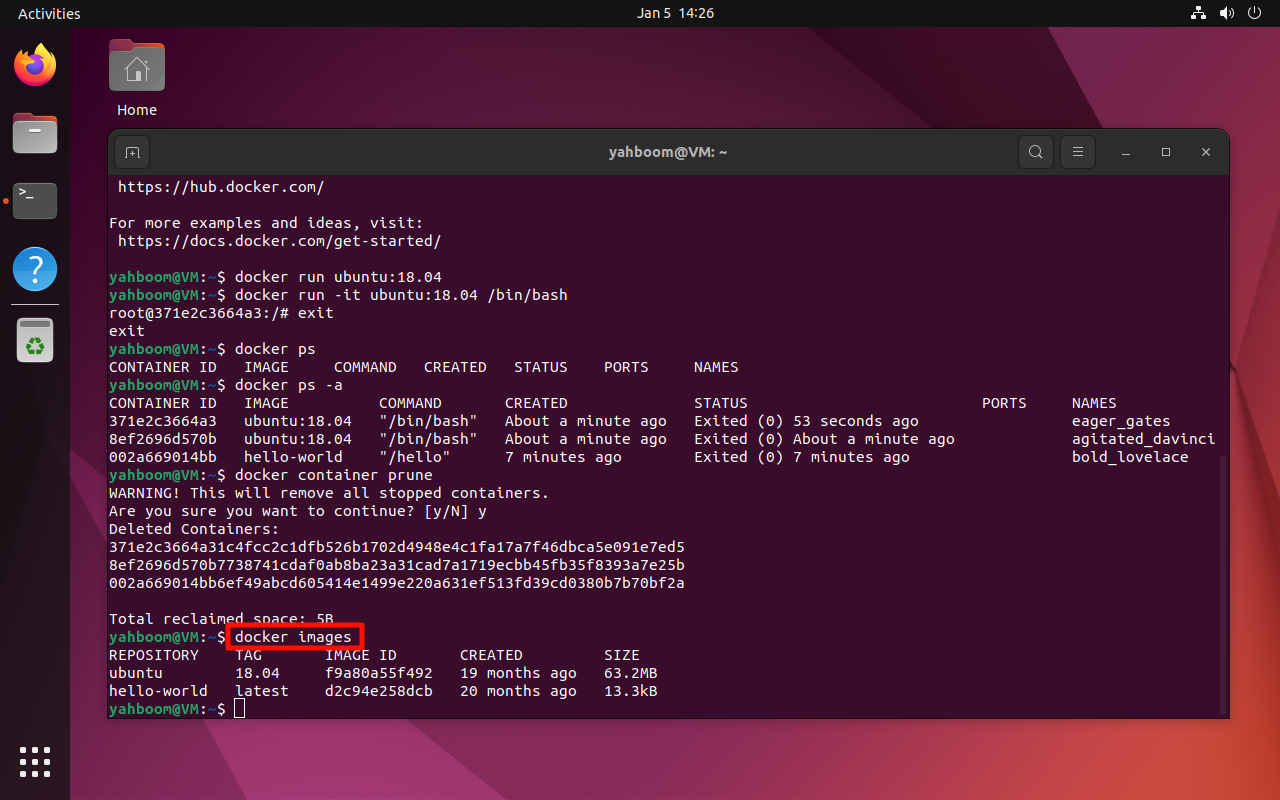
6. View Local Images
docker images
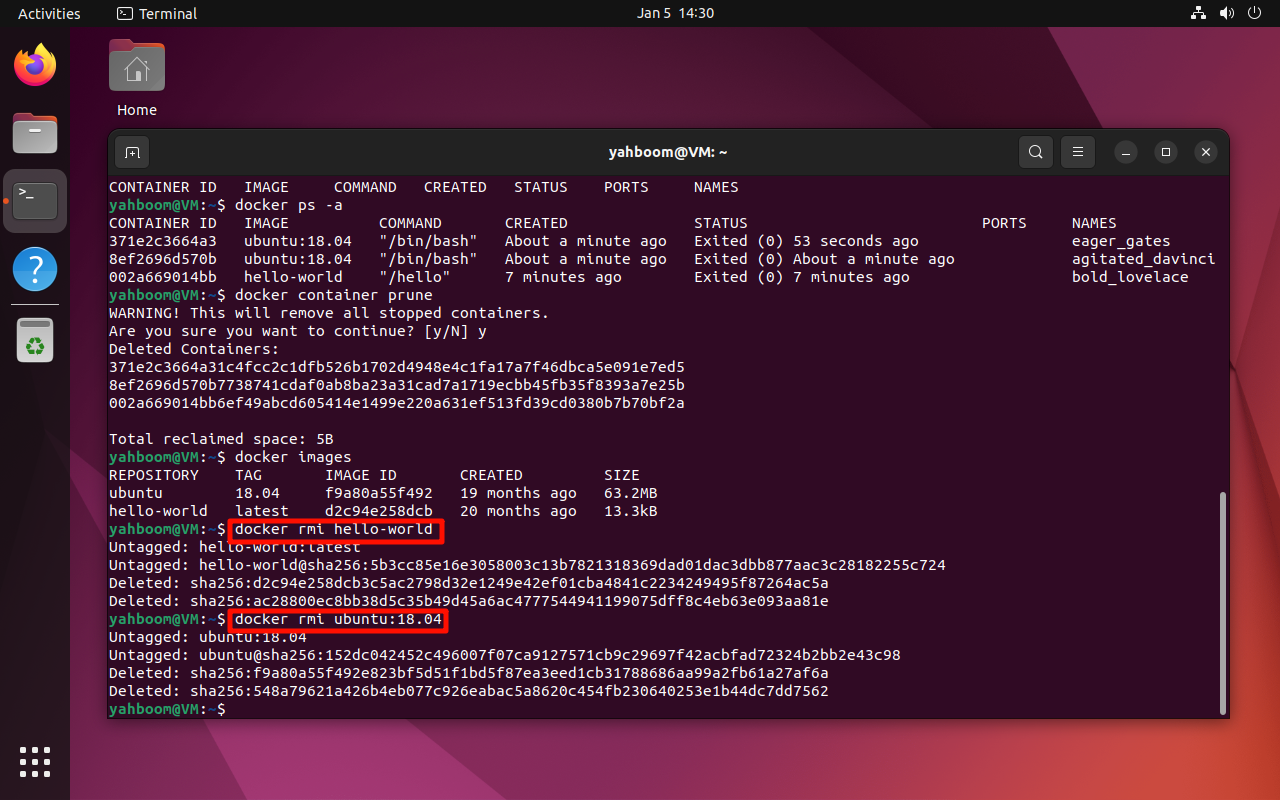
7. Delete Images
warning
The image must not be used by any running container before deletion.
Delete an image:
docker rmi <image_name>
Examples:
docker rmi hello-world
docker rmi ubuntu:18.04
8. Commit a Container as an Image
Run a container interactively:
docker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash
Commit the container as a new image:
docker commit <CONTAINER_ID> <image_name>:<tag>
note
Replace <CONTAINER_ID> with the actual container ID from
docker ps -a.
9. Stop a Container
docker stop <container_id>
10. Access a Running Container from Multiple Terminals
docker exec -it <container_id> /bin/bash
Maintained by HemiHex.