7. Client
In ROS communication, in addition to topic communication, there is also a type of service communication. Services include both client and server, where the client requests the service and the server provides the service. This section explains how to implement a client using C++ and Python.
7.1 Preparation Work
7.1.1 Establishing a Function Package
- Switch to the
~/catkin_ws/srcdirectory:
catkin_create_pkg learning_server std_msgs rospy roscpp geometry_msgs turtlesim
- Switch to the
~/catkin_wsdirectory:
catkin_make
7.2 C++ Language Implementation
7.2.1 Implementation Steps
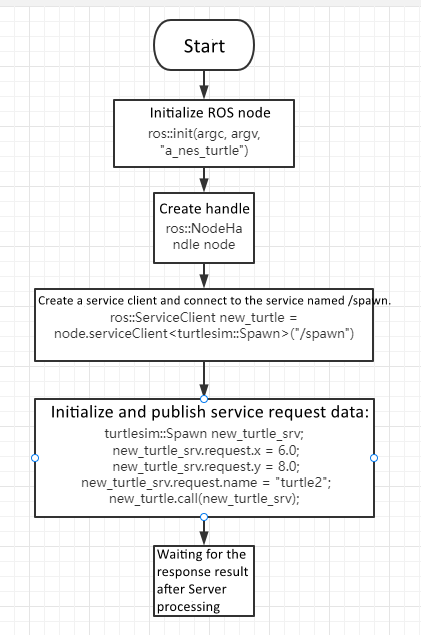
- Initialize the ROS node\
- Create a node handle\
- Create a client instance\
- Initialize and send service request data\
- Wait for the server response
7.2.2 Create the Client Program
Create a new C++ file under server/src:
a_new_turtle.cpp
Paste the following code:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <turtlesim/Spawn.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "a_new_turtle"); // Initialize ROS node
ros::NodeHandle node;
ros::service::waitForService("/spawn"); // Wait for spawn service
ros::ServiceClient new_turtle =
node.serviceClient<turtlesim::Spawn>("/spawn");
turtlesim::Spawn new_turtle_srv;
new_turtle_srv.request.x = 6.0;
new_turtle_srv.request.y = 8.0;
new_turtle_srv.request.name = "turtle2";
ROS_INFO("Call service to create a new turtle named %s at (%.1f, %.1f)",
new_turtle_srv.request.name.c_str(),
new_turtle_srv.request.x,
new_turtle_srv.request.y);
new_turtle.call(new_turtle_srv);
ROS_INFO("Spawn turtle successfully [name: %s]",
new_turtle_srv.response.name.c_str());
return 0;
}
Process Flow Diagram
CMakeLists.txt Configuration
Add the following under the build section:
add_executable(a_new_turtle src/a_new_turtle.cpp)
target_link_libraries(a_new_turtle ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
Compile the Workspace
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
Run the Program
roscore
rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node
rosrun learning_server a_new_turtle
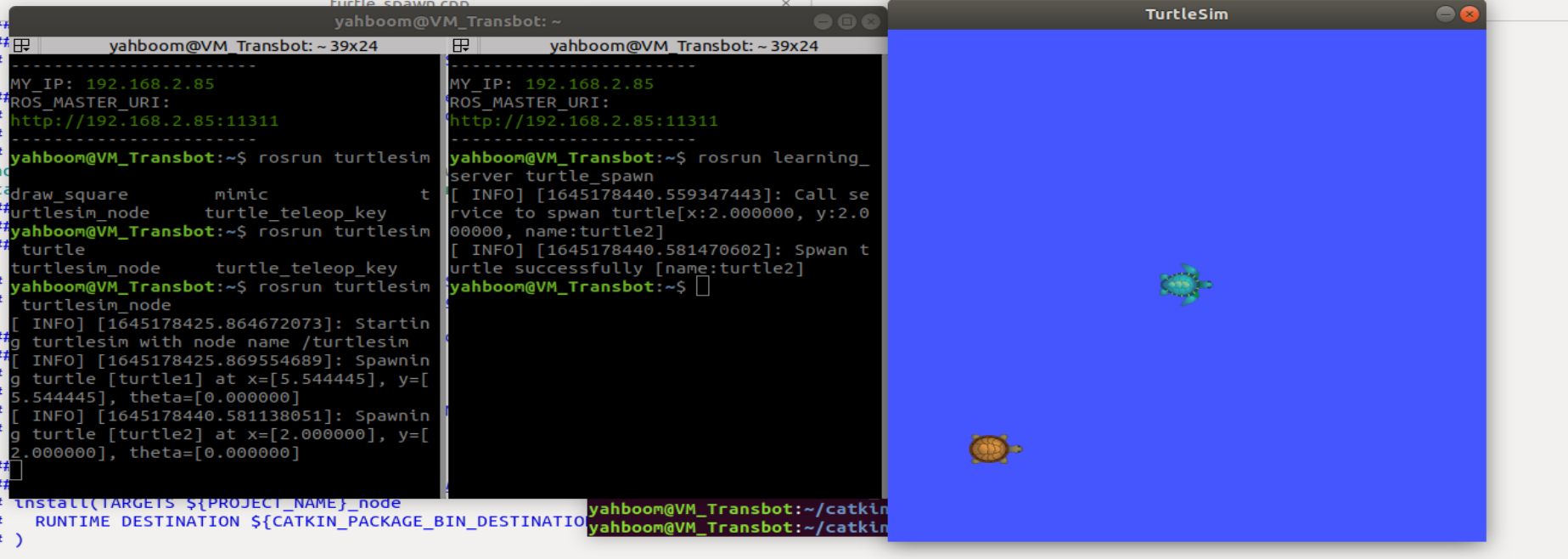
Program Output Example
Program Description
After starting the turtle simulation node, running the a_new_turtle
program will create another turtle on the screen. This is done by
calling the /spawn service provided by the turtle node.
To view all available services:
rosservice list
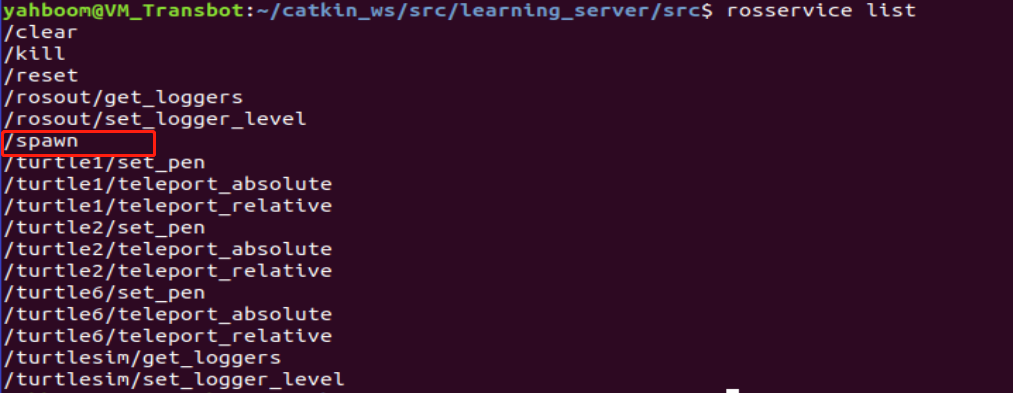
To inspect the /spawn service:
rosservice info /spawn
The parameters required are:
xythetaname
These are initialized in the client program as:
srv.request.x = 6.0;
srv.request.y = 8.0;
srv.request.name = "turtle2";
7.3 Python Language Implementation
7.3.1 Create the Client Script
Under server/scripts, create the following file:
a_new_turtle.py
Paste the following content:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import rospy
from turtlesim.srv import Spawn
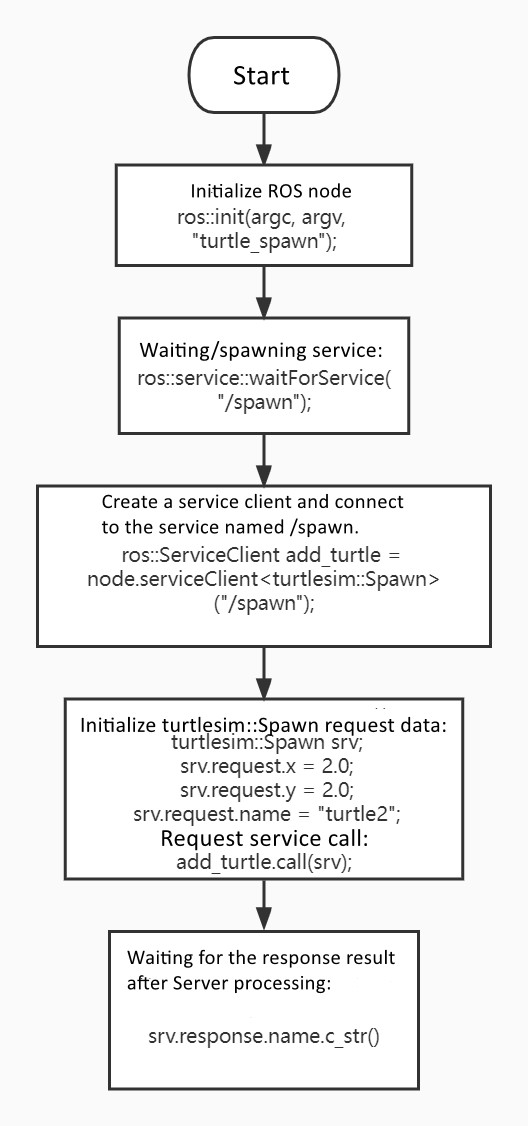
def turtle_spawn():
rospy.init_node('new_turtle') # Initialize ROS node
rospy.wait_for_service('/spawn') # Wait for spawn service
try:
new_turtle = rospy.ServiceProxy('/spawn', Spawn)
response = new_turtle(2.0, 2.0, 0.0, "turtle2")
return response.name
except rospy.ServiceException as e:
print("Failed to call service: %s" % e)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("A new turtle named %s." % turtle_spawn())
Python Program Flow Diagram