1. Introduction to ROS 2
1. Overview of ROS 2
ROS 2 is the second-generation Robot Operating System, an upgrade to ROS 1 that addresses many of its limitations. The first ROS 2 release, Arden, was published in 2017. Through continuous updates and optimizations, ROS 2 now has stable long-term support releases.
As with ROS 1, the Linux distribution version must match the ROS 2 version. The corresponding versions are shown below.
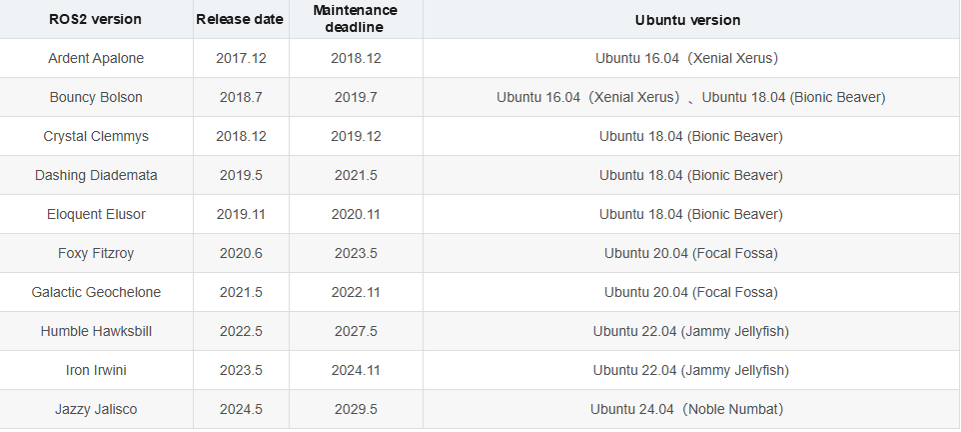
Download the appropriate ROS 2 version for your Linux distribution. This course uses the Humble version as the reference. The programs and examples provided in this course are applicable across all ROS 2 versions.
2. Features of ROS 2
2.1 Full Multi-Platform Support
ROS 2 fully supports the following platforms:
- Ubuntu\
- macOS\
- Windows 10
2.2 Distributed Architecture
The ROS master node has been eliminated. ROS 2 enables distributed node discovery, publish/subscribe, and request/response communication without a centralized master.
2.3 Real-Time Support
ROS 2 introduces built-in support for real-time systems, making it suitable for industrial and safety-critical robotics applications.
2.4 New Programming Language Standards
- C++11
- Python 3.5+
2.5 New Build System
ROS 2 uses the Ament build system (replacing Catkin from ROS 1).
2.6 ROS 1 and ROS 2 Interoperability
ROS 1 can communicate with ROS 2 via rosbridge, allowing hybrid system deployments.
3. Differences Between ROS 2 and ROS 1
3.1 Platform Support
ROS 1 primarily supports Linux and is most commonly used on Ubuntu.
ROS 2 supports:
- Ubuntu
- Windows
- Embedded development boards
This makes ROS 2 far more flexible for modern deployments.
3.2 Programming Language
C++
ROS 1 core is based on C++03, whereas ROS 2 is built extensively on C++11.
Python
- ROS 1 uses Python 2
- ROS 2 requires Python 3.5+
- ROS 2 Foxy uses Python 3.8
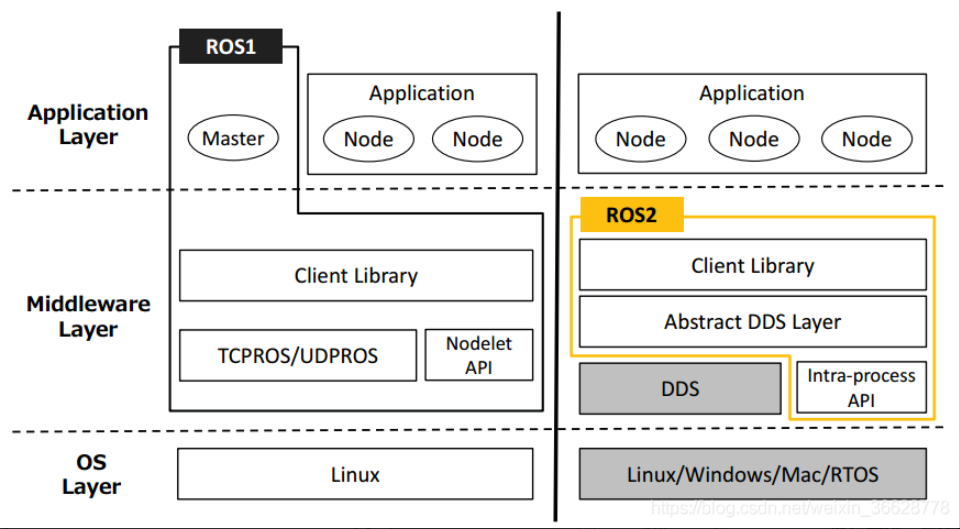
3.3 Middleware
ROS 1 requires starting roscore before any node can communicate. This
master node handles all inter-node messaging.
ROS 2 completely removes this dependency. Instead, it introduces an abstract middleware interface based on the DDS (Data Distribution Service) standard. This allows ROS 2 to support:
- Multiple QoS (Quality of Service) policies
- High-reliability communication
- Operation over different network types
3.4 Compilation Commands
- ROS 1:
catkin_make\ - ROS 2:
colcon build
ROS 2 adopts colcon as its official build tool for faster and more
scalable builds.