6. ROS 2 Nodes
1. Node Introduction
Regardless of the communication method used, all ROS 2 communication
relies on nodes.
Each node typically represents a single functional module. For example:
- A radar driver node publishes radar scan data.
- A camera driver node publishes image messages.
A complete robot system may run many nodes simultaneously.
A single executable file (C++ or Python) can contain one or more
nodes.
2. Node Creation Process
- Create a program file\
- Import necessary ROS 2 libraries\
- Implement node logic\
- Configure package metadata\
- Compile and run the node
3. Hello World Node Example (Python)
3.1 Creating the Python Package
Replace workspace with your actual workspace path:
cd workspace/src
ros2 pkg create pkg_helloworld_py --build-type ament_python --dependencies rclpy --node-name helloworld
3.2 Writing the Node Code
A template file helloworld.py will be generated.
Replace its contents with the following code:
import rclpy # ROS 2 Python client library
from rclpy.node import Node # Base Node class
import time
"""
Create a HelloWorld node and log 'Hello World' periodically.
"""
class HelloWorldNode(Node):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__(name) # Initialize parent Node
while rclpy.ok(): # Keep running while ROS 2 is active
self.get_logger().info("Hello World")
time.sleep(0.5) # Loop delay
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args) # Initialize ROS 2 system
node = HelloWorldNode("helloworld")
rclpy.spin(node) # Keep node alive
node.destroy_node() # Cleanup
rclpy.shutdown() # Shutdown ROS 2
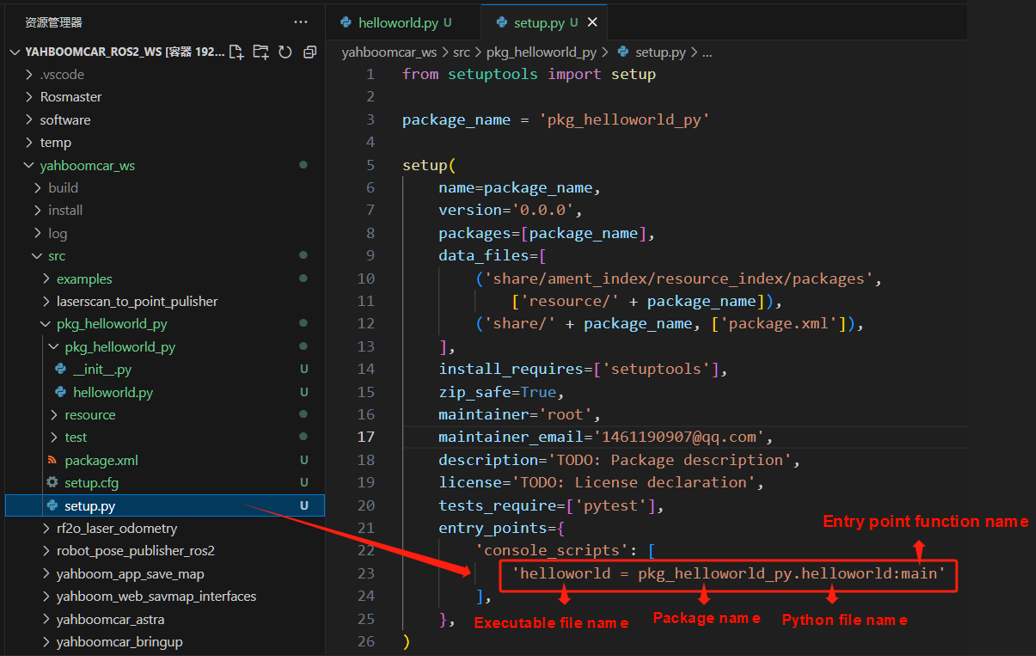
Adding Entry Points in setup.py
Open the package's setup.py and add:
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'helloworld = pkg_helloworld_py.helloworld:main'
],
},
3.3 Compiling the Package
Compile only the new package:
colcon build --packages-select pkg_helloworld_py
Refresh the workspace environment:
source install/setup.bash
3.4 Running the Node
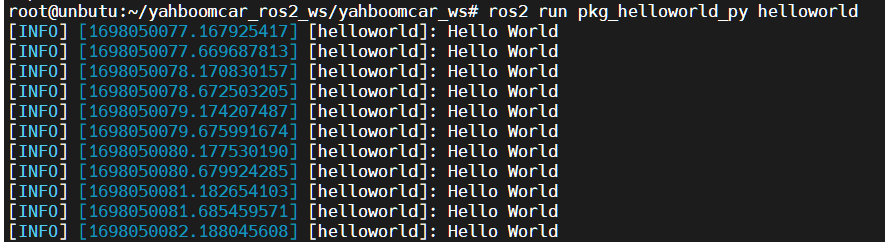
ros2 run pkg_helloworld_py helloworld
If successful, you will see recurring output: