8. ROS 2 Service Communication
1. Introduction to Service Communication
Service communication is a request-response communication model. The client sends a request to the server, and the server responds with data.
This follows the Client/Server (CS) communication model.
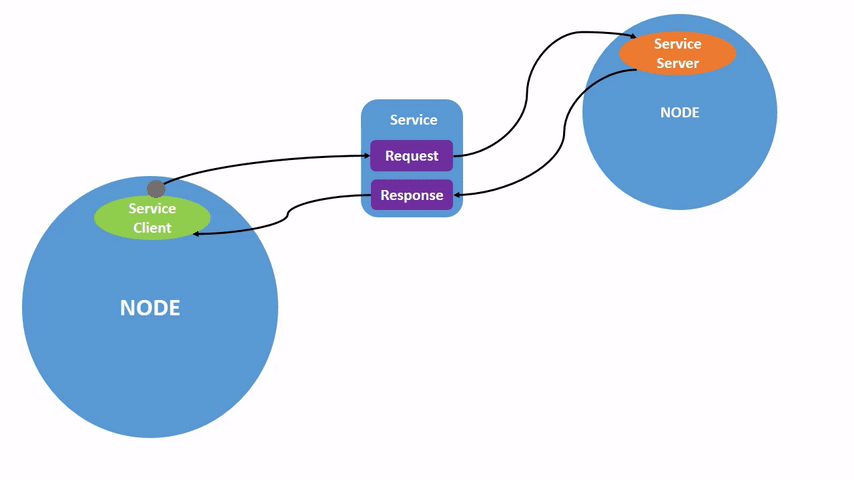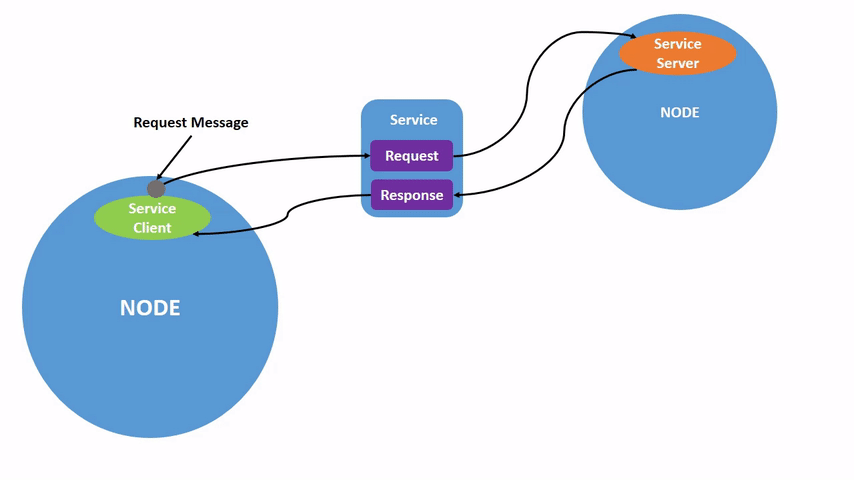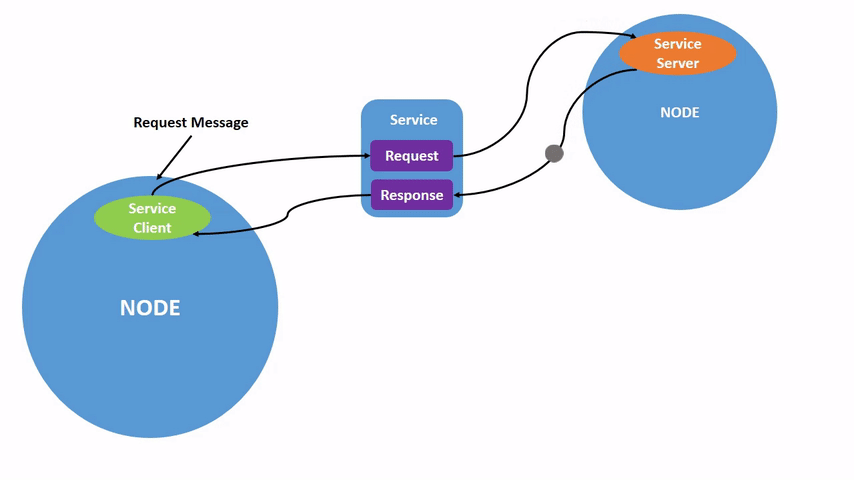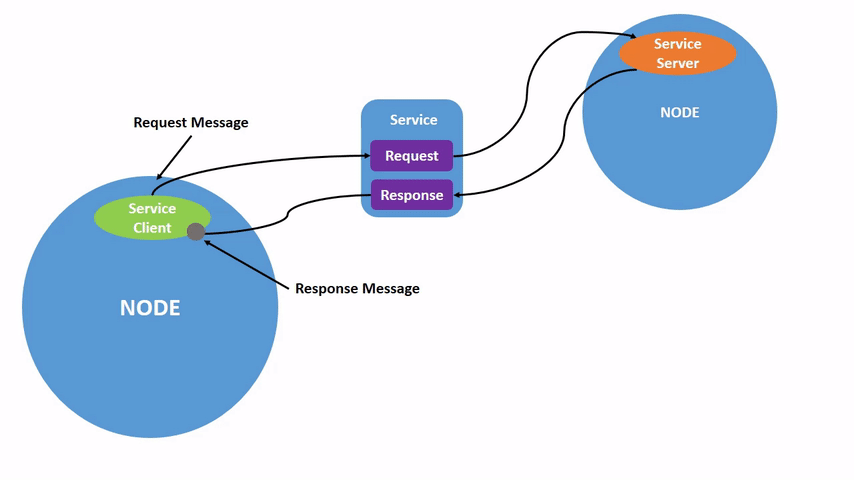
In this model: - The client requests data. - The server processes the request and returns a response.
A common real-world example is a web browser requesting data from a website server.
2. Create a New Package
Navigate to the src directory of your ROS 2 workspace and run:
ros2 pkg create pkg_service --build-type ament_python --dependencies rclpy --node-name server_demo
After execution, the pkg_service package and server_demo node will
be created.
3. Server Implementation
3.1 Creating the Server
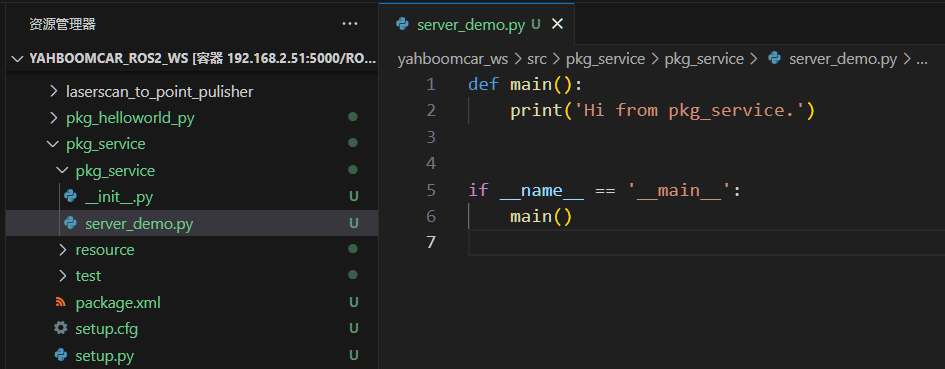
Edit server_demo.py and add the following code:
# Import related libraries
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from example_interfaces.srv import AddTwoInts
class Service_Server(Node):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__(name)
self.srv = self.create_service(AddTwoInts, '/add_two_ints', self.Add2Ints_callback)
def Add2Ints_callback(self, request, response):
response.sum = request.a + request.b
print("response.sum =", response.sum)
return response
def main():
rclpy.init()
server_demo = Service_Server("publisher_node")
rclpy.spin(server_demo)
server_demo.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
3.2 Viewing the Service Interface
To view the structure of the service message:
ros2 interface show example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts
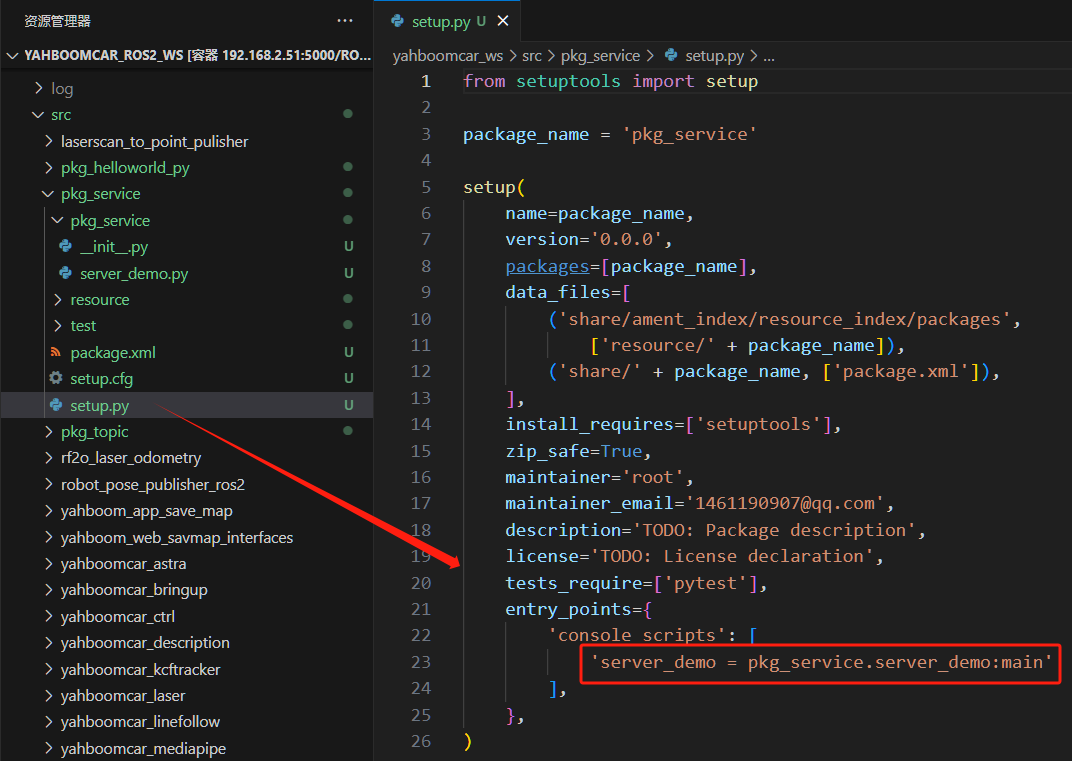
3.3 Editing the Configuration File
Open setup.py and add:
'server_demo = pkg_service.server_demo:main',
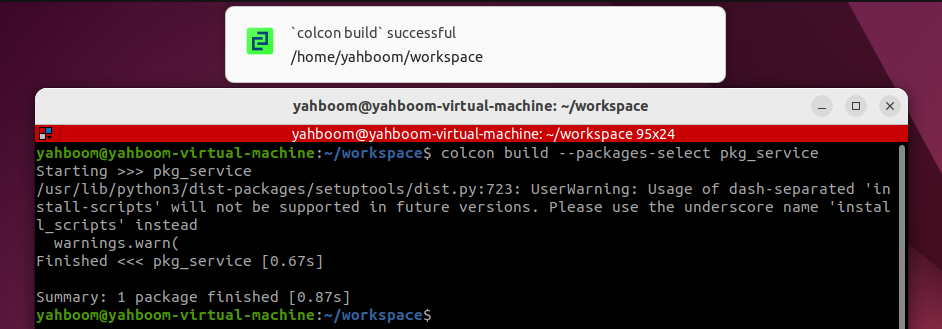
3.4 Compiling the Package
colcon build --packages-select pkg_service
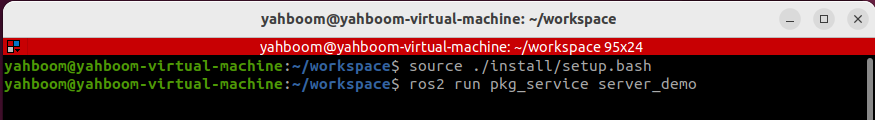
3.5 Running the Server
ros2 run pkg_service server_demo
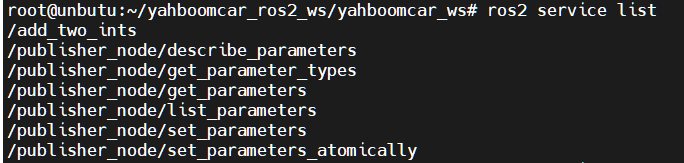
List services:
ros2 service list
Call the service:
ros2 service call /add_two_ints example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts "{a: 1, b: 4}"

4. Client Implementation
4.1 Creating the Client
Create client_demo.py in the same directory as server_demo.py.
Add the following code:
# Import related libraries
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from example_interfaces.srv import AddTwoInts
class Service_Client(Node):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__(name)
self.client = self.create_client(AddTwoInts, '/add_two_ints')
while not self.client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=1.0):
print("Waiting for service...")
self.req = AddTwoInts.Request()
self.send_request()
def send_request(self):
self.req.a = 3
self.req.b = 6
self.future = self.client.call_async(self.req)
self.future.add_done_callback(self.response_callback)
def response_callback(self, future):
try:
response = future.result()
print(f"Service Response: {response.sum}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Service call failed: {e}")
def main():
rclpy.init()
client_demo = Service_Client("client_node")
rclpy.spin(client_demo)
client_demo.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
This completes ROS 2 service communication using Python.